October 22, 2025
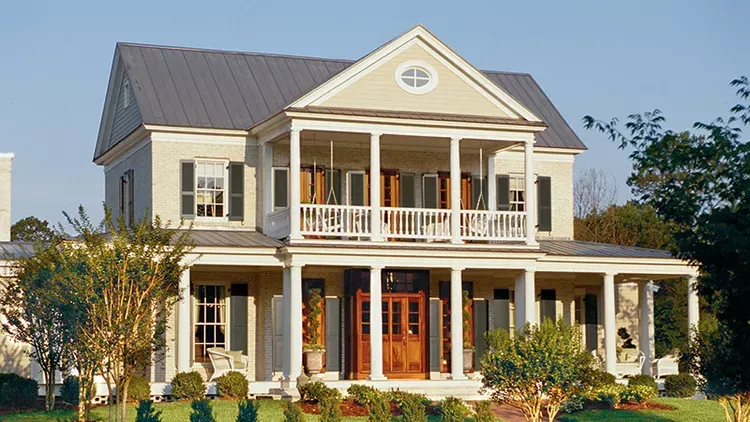
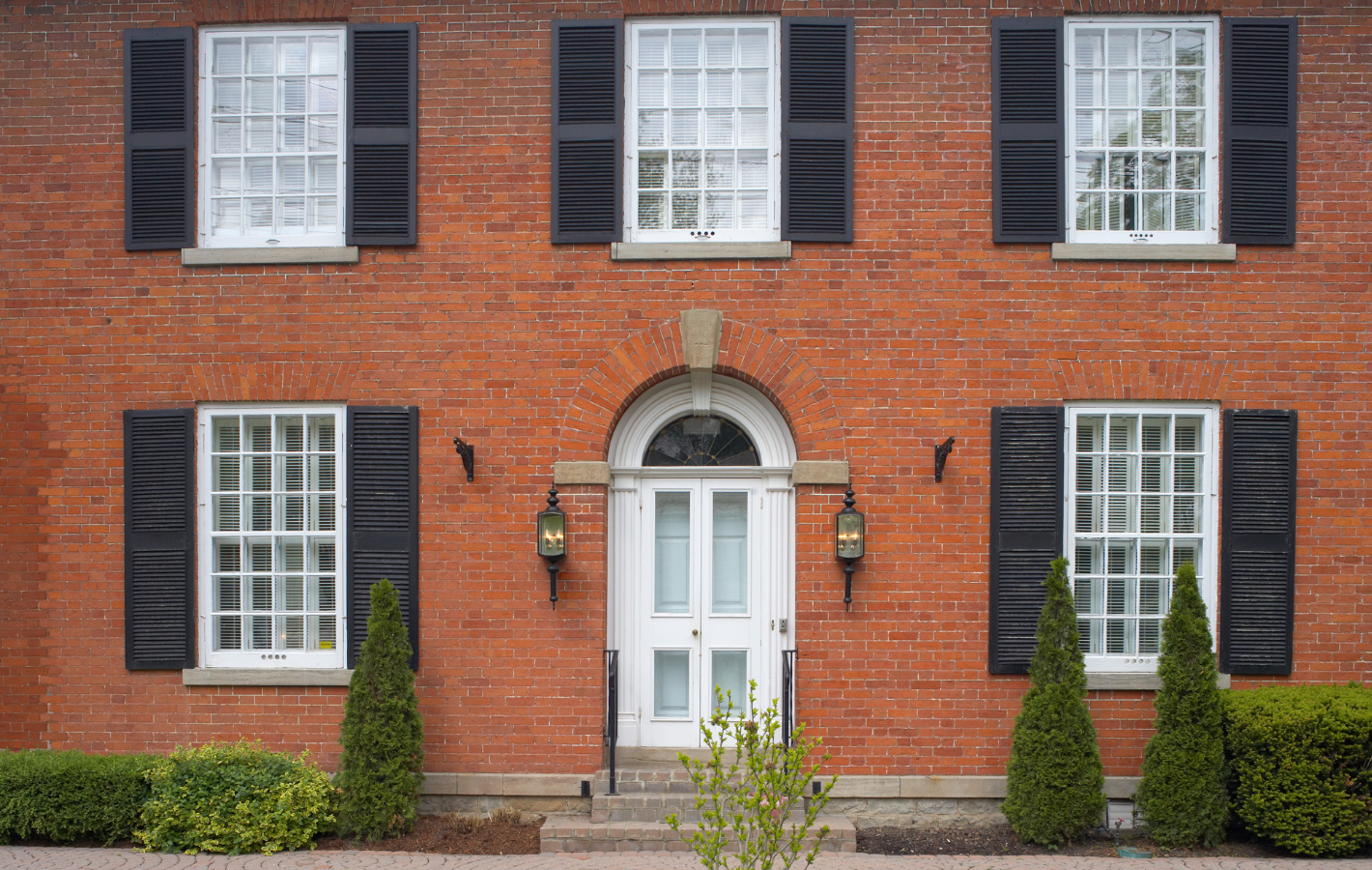
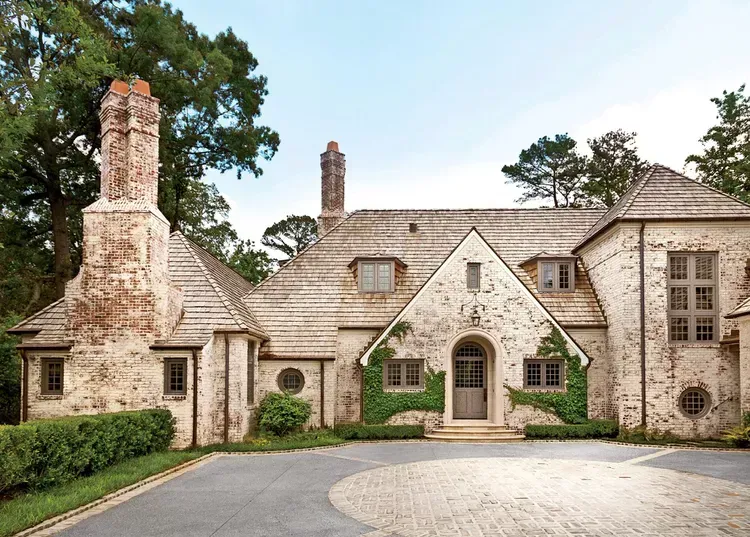
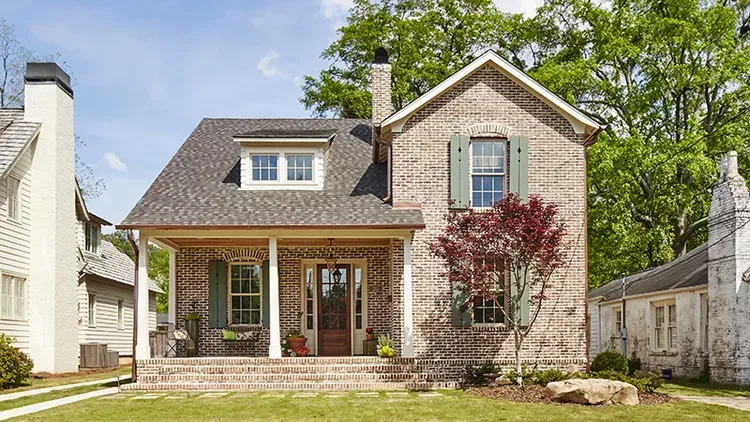
When it comes to building or renovating a home, one of the most important decisions you'll make is selecting the right building material. The choice you make will not only influence the aesthetic appeal of your home but also its durability, energy efficiency, and overall value. Among the myriad of options available, brick has long been a favored material due to its timeless appeal and robust characteristics. However, other materials like wood, concrete, vinyl siding, and steel also present compelling advantages. This blog will compare brick with these alternative materials, examining factors such as durability, cost, energy efficiency, maintenance, and aesthetic appeal to help you make the best choice for your home. Comparing Durability 1. Bricks Bricks are renowned for their durability and longevity. Made from natural clay or shale and fired at high temperatures, bricks are resistant to the elements, including extreme weather conditions, fire, and pests. A well-constructed brick home can last for centuries with minimal maintenance. The dense nature of bricks makes them less susceptible to cracking and warping, which are common issues with other materials. Additionally, bricks do not rot, rust, or get damaged by termites, making them an ideal choice for long-term structural integrity. 2. Wood Wood is a traditional building material that offers natural beauty and warmth. However, wood is highly susceptible to damage from moisture, insects (especially termites), and fire. Over time, wood can warp, rot, or crack, particularly in areas with high humidity or frequent rainfall. To maintain its durability, wood requires regular treatments such as staining, sealing, or painting, which adds to the long-term maintenance costs. While wood can last a long time if properly cared for, it generally does not offer the same level of durability as brick. 3. Concrete Concrete is a strong and durable material commonly used in modern construction. It is particularly resistant to fire and extreme weather conditions. However, concrete can be prone to cracking over time due to thermal expansion and contraction, as well as settling of the ground beneath it. While concrete is durable, it lacks the aesthetic appeal of brick and can be challenging to repair once cracks appear. Additionally, concrete is less flexible than wood or steel, making it more vulnerable to damage in areas with significant ground movement. 4. Vinyl Siding Vinyl siding is a popular choice for homeowners due to its affordability and low maintenance requirements. However, it is less durable than brick or concrete. Vinyl siding can crack, fade, or warp over time, particularly when exposed to extreme temperatures. It is also susceptible to damage from high winds, hail, and impacts. While vinyl siding can last for several decades with proper care, it does not offer the same level of long-term durability as brick or concrete. 5. Steel Steel is an incredibly durable material, especially when it comes to structural support. It is resistant to fire, termites, and decay, making it a reliable choice for building. However, steel is susceptible to rust if not properly treated, especially in coastal areas with high humidity and salt exposure. Additionally, steel can be prone to thermal expansion, which may cause warping or bending over time. While steel offers excellent structural durability, it is often used in conjunction with other materials like brick or concrete to achieve the desired aesthetic and insulation properties. Energy Efficiency 1. Bricks Bricks excel in terms of energy efficiency due to their high thermal mass. Thermal mass refers to a material's ability to absorb, store, and release heat. Brick walls can help regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling. This natural temperature regulation can lead to significant energy savings, particularly in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations. Additionally, bricks provide excellent insulation against noise, making homes quieter and more comfortable. 2. Wood Wood is a natural insulator, offering good energy efficiency in terms of keeping heat in during the winter and out during the summer. However, wood's energy efficiency can be compromised by gaps, cracks, and warping over time, which can lead to drafts and higher energy costs. Insulation can be added to wood-framed homes to improve energy efficiency, but it may not be as effective as the thermal mass provided by brick. 3. Concrete Concrete also has good thermal mass properties, similar to brick. It can absorb and release heat, helping to stabilize indoor temperatures. However, concrete alone is not a good insulator, and additional insulation is often required to achieve energy efficiency comparable to brick. Concrete's energy efficiency can be enhanced by using insulated concrete forms (ICFs), which incorporate insulation into the concrete walls, but this adds to the overall cost of the construction. 4. Vinyl Siding Vinyl siding on its own offers very little in terms of insulation and thermal mass. To improve energy efficiency, vinyl siding is often paired with insulated backing or foam insulation. While this can enhance the energy efficiency of a home, it still may not match the performance of brick or concrete. Vinyl siding also lacks the noise insulation properties of brick, making it less effective at reducing outside noise. 5. Steel Steel is not known for its energy efficiency. It has a low thermal mass and can conduct heat and cold, leading to higher energy costs if not properly insulated. Steel-framed homes often require additional insulation to achieve the desired energy efficiency, which can add to the overall cost of construction. While steel is strong and durable, it does not naturally provide the same energy efficiency benefits as brick or wood. Cost Considerations 1. Bricks The upfront cost of building with brick is generally higher than other materials like wood or vinyl siding. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term savings in maintenance and energy efficiency. Brick homes require minimal upkeep and have lower energy costs due to their thermal mass. Additionally, brick homes tend to have higher resale values, making them a worthwhile investment in the long run. 2. Wood Wood is a relatively affordable building material, especially for framing and siding. However, the cost of maintaining a wood home can add up over time. Regular painting, staining, and repairs are necessary to protect wood from the elements and pests. The initial savings on wood construction can be outweighed by the long-term maintenance costs, particularly in regions with harsh weather conditions. 3. Concrete Concrete is a cost-effective material, particularly for foundations and structural elements. The cost of concrete can vary depending on the type of construction and the need for additional insulation. While concrete is durable and low-maintenance, the initial cost of building with concrete can be higher than wood or vinyl siding. However, concrete's longevity and low maintenance requirements can lead to cost savings over time. 4. Vinyl Siding Vinyl siding is one of the most affordable building materials available, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious homeowners. The low cost of vinyl siding is complemented by its low maintenance requirements, as it does not need to be painted or stained. However, vinyl siding's lower durability and energy efficiency may result in higher costs in the long term, particularly if repairs or replacements are needed. 5. Steel Steel is generally more expensive than wood or vinyl siding, particularly when used for structural framing. The cost of steel construction can be higher due to the need for additional insulation and rust prevention treatments. However, steel's durability and strength can make it a cost-effective choice for long-term structural support, especially in commercial or industrial buildings. In residential construction, steel is often combined with other materials like brick to achieve a balance of durability, insulation, and aesthetic appeal. Aesthetic Appeal 1. Bricks Bricks offer a timeless aesthetic that can complement a wide range of architectural styles, from traditional to modern. The natural variations in color, texture, and size give brick homes a unique character that is difficult to replicate with other materials. Bricks can be used to create intricate patterns and designs, adding depth and interest to a home's exterior. The aesthetic appeal of brick extends to interiors as well, with exposed brick walls becoming increasingly popular in modern home design. 2. Wood Wood is prized for its natural beauty and warmth. It can be stained or painted in a variety of colors to match the homeowner's preferences. Wood's versatility allows it to be used in both traditional and contemporary designs, and it can be easily customized with decorative elements like trim and moldings. However, wood's aesthetic appeal can be diminished over time if not properly maintained, as it is prone to fading, warping, and decay. 3. Concrete Concrete offers a more utilitarian aesthetic, often associated with modern and industrial designs. While concrete can be finished in various textures and colors, it lacks the natural warmth of wood or the classic charm of brick. However, concrete's minimalist aesthetic can be appealing in contemporary architecture, particularly when paired with other materials like glass and steel. Decorative techniques like stamping, staining, and polishing can enhance the visual appeal of concrete, but these add-ons can increase the overall cost. 4. Vinyl Siding Vinyl siding is available in a wide range of colors and styles, making it a versatile option for homeowners looking to achieve a specific look. However, vinyl siding often lacks the depth and texture of natural materials like brick or wood. While it can mimic the appearance of wood, stone, or brick, the imitation is often noticeable, and the overall aesthetic can feel less authentic. Vinyl siding is best suited for homeowners seeking a low-maintenance, budget-friendly option with a clean, modern appearance. 5. Steel Steel's aesthetic appeal is often associated with modern, industrial, or minimalist designs. Its sleek, clean lines and metallic finish can create a striking contrast with other materials like wood or brick. However, steel can also appear cold or utilitarian if not balanced with warmer elements. In residential construction, steel is often used in combination with other materials to soften its appearance and add visual interest.