Expert Team
Our phenomenal team of experts is dedicated to providing personalized guidance and expertise to assist your construction needs.
Professional Affiliations
Magnolia Brick proudly aligns itself with prestigious organizations such as the Brick Institute of America, Home Builders Association, and Community Development Foundation, reinforcing our commitment to industry excellence.
Quality Assurance
At Magnolia Brick, our unwavering commitment is to meticulously source high-quality materials from industry-leading manufacturers, ensuring the utmost excellence in your construction projects.
What Makes Brick so Timeless & Classic?
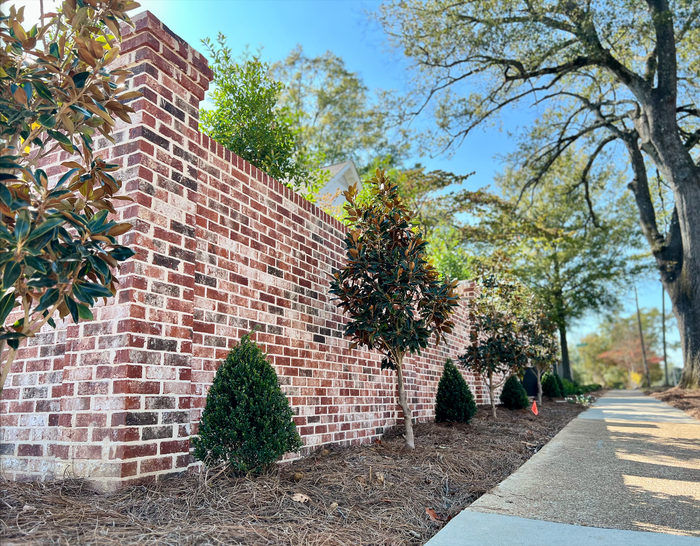
01 Durability
Brick is incredibly durable and long-lasting. Many historic buildings made of brick are still standing strong after centuries, showcasing its ability to withstand the test of time. It resists weathering, pests, and fire, making it a reliable choice for construction.
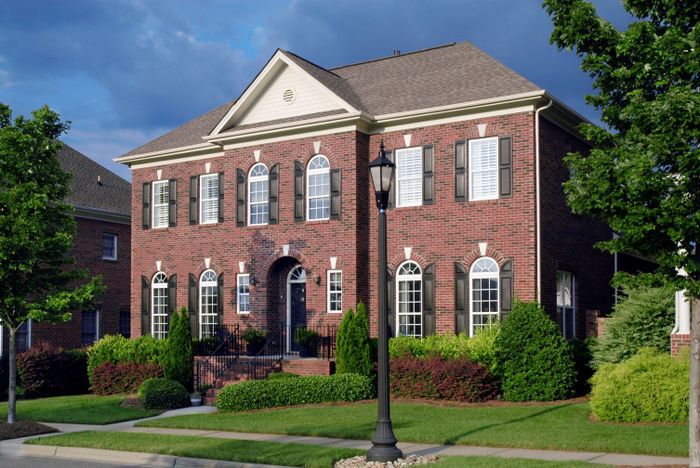
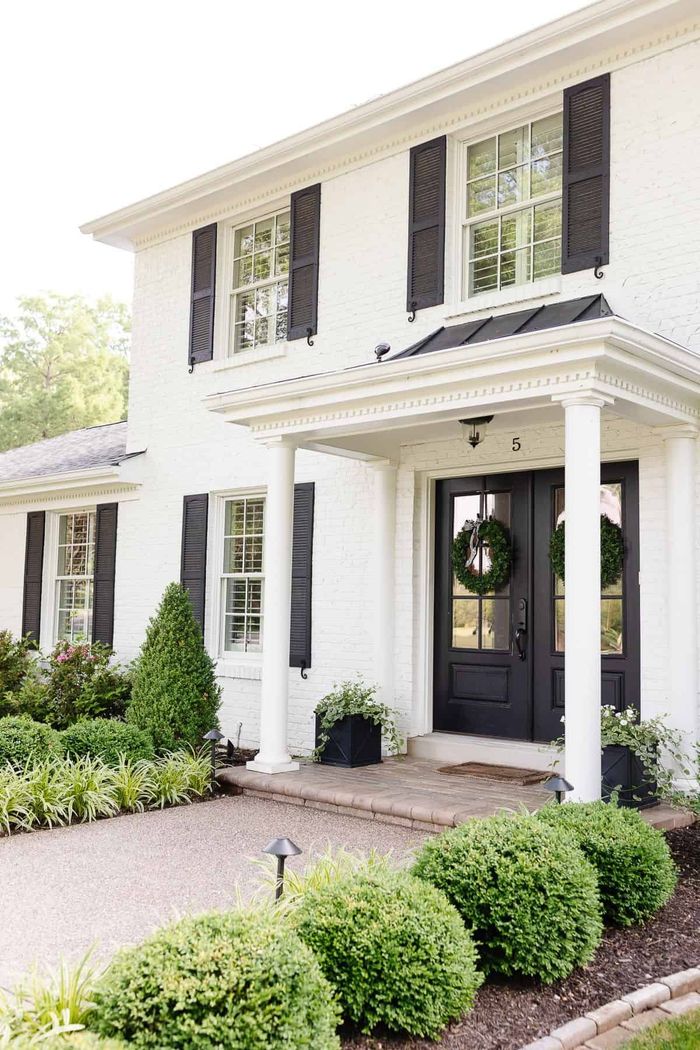
02 Aesthetic Appeal
The earthy, warm, and natural look of brick appeals to a wide range of architectural styles. It can be used in both traditional and contemporary designs, offering a timeless and versatile aesthetic that complements various building types.
03 Color Variety
Bricks come in a wide array of colors, from reds and browns to greys and whites. This versatility in color allows architects and builders to select bricks that match the specific design and ambiance they want to achieve.